
Local governments are increasingly exploring generative AI (genAI) to streamline services for constituent engagement, administrative support, and improved data analytics, among other cases. Though many local governments are interested in this innovation, many lack awareness (PDF) of the full benefits of genAI, how their peers are using it, and where to begin.
We conducted research to understand current opportunities, challenges, and unmet needs for local government use of genAI. Through this work, we developed a framework that maps local government genAI use cases into the three tiers shown below. The tiers range from the most basic and accessible genAI use (tier 1) to the most complex and potentially transformative genAI use (tier 3).
Local Governments’ Use of GenAI Falls into Three Tiers That Increase in Complexity
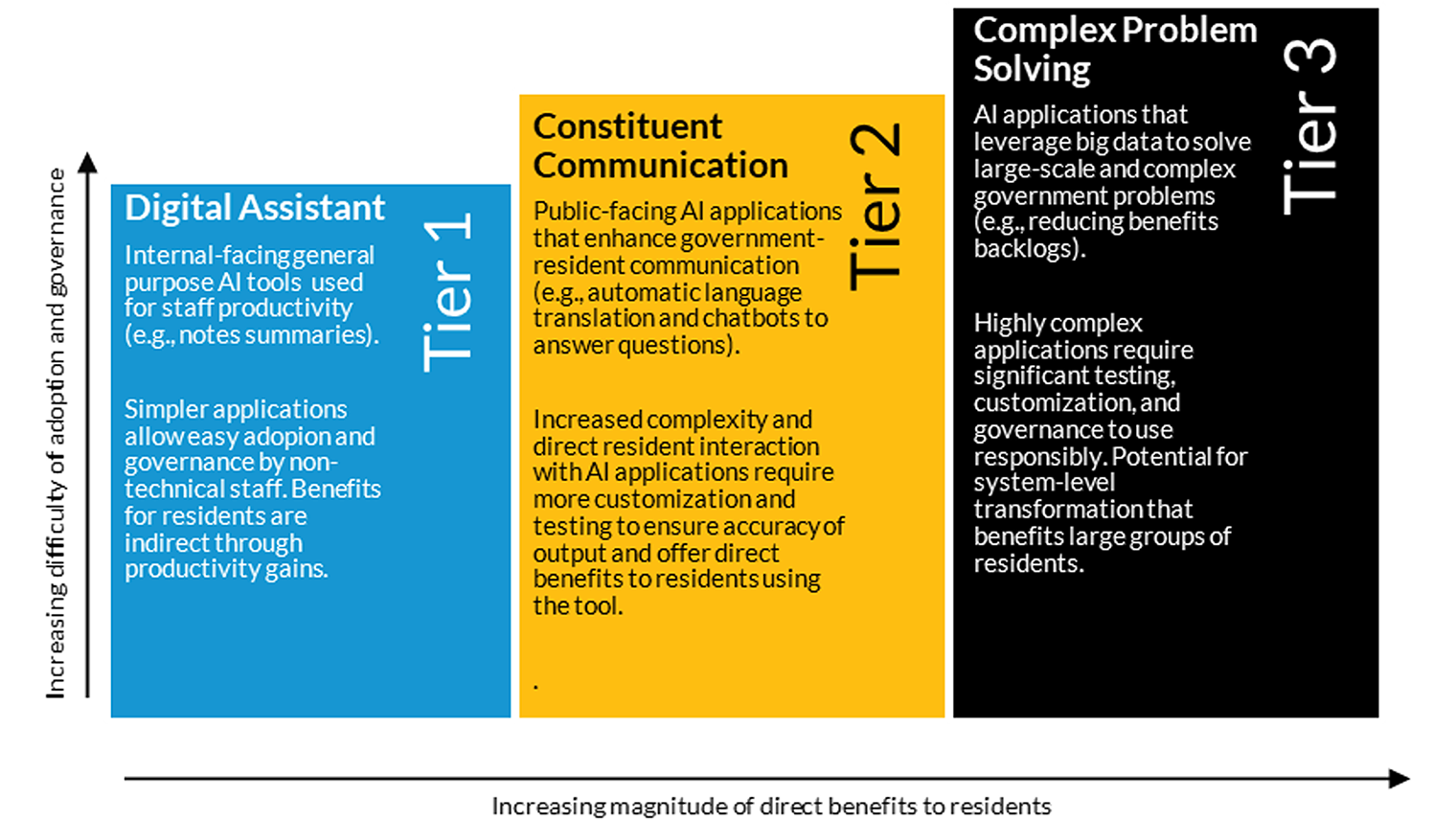
Source: Authors’ rendering based on interview findings.
This framework can help local governments effectively navigate the landscape of genAI to identify applications that can meet their needs. Understanding which tier a genAI application or potential use case falls within can help local governments understand the capacity and guardrails they need to build before adopting genAI to ensure responsible and beneficial use.
How are the tiers defined?
Tier 1 AI applications leverage genAI as digital assistants to help automate routine tasks and increase the productivity of government staff, helping governments bridge critical staffing gaps. We found that current local government genAI use is largely exploratory and concentrated in this tier, because tier 1 applications are less costly to adopt and their governance and accountability structures that ensure ethical and fair use are easier to implement.
Many tier 1 use cases leverage general genAI tools that are free, are baked into software that governments already use (like Microsoft CoPilot or Google Gemini), or are tailored to government privacy and cybersecurity requirements, such as the recently released ChatGPT Gov.
Tier 2 AI applications help local governments more effectively communicate with residents and help residents more seamlessly navigate government information. Examples include real-time translation of 911 calls and chatbots on government websites that answer residents’ questions about services and more efficiently direct them to needed resources. This tier poses greater oversight and accountability challenges than tier 1 because the AI-generated output is delivered directly to residents, without government officials being able to impose quality assurance.
Tier 3 AI applications leverage big data to solve complex government problems. This tier of genAI applications could have a transformative impact on policy and service delivery, such as by closing harmful benefit application backlogs, facilitating enrollment in government services and benefits, and safely accelerating housing production to address housing shortages.
For example, tier 3 genAI applications could help address barriers in access to public benefits by reading and summarizing benefit eligibility rules and scanning applications to confirm they contain all required information. To achieve these applications’ potential benefits, local governments will need to effectively govern AI tools, which is particularly challenging given the complexity and scale of applications in this tier.
How can local governments adopt more complex genAI uses?
Before implementing genAI at any tier, local governments should develop an AI policy framework to ensure safe use and establish guardrails to make staff comfortable exploring genAI.
At a minimum, an AI framework should establish permissible and prohibited uses, information that can be provided to genAI, human oversight and review mechanisms, ethical guidelines, transparency standards, and processes for updating guidance. Local governments can look to AI policy examples from other cities (such as Tempe, Arizona; San Jose, California; and Boston) or policy templates (PDF) to draft their policy. Governments should also invest in building high-level AI literacy through local government–tailored resources, such as knowledge-sharing platforms, trainings, and toolkits that support responsible and effective genAI use.
Adopting tier 2 and 3 applications requires local governments to implement more in-depth guardrails (such as tailored policies for specific uses) and specialized capacity. Some state and local governments, including New York (PDF) and Massachusetts, have adopted chatbot regulations that ensure users are aware they’re interacting with AI and hold chatbot providers accountable if chatbot communications are misleading or deceptive.
Tier 2 and 3 applications are more specialized and interact directly with residents. Before implementing these applications, it’s critical to vet the quality of tailored tools and assess how applicable generalized tools are to specific use cases. This vetting can be prohibitively resource intensive for local governments because of the crowded and rapidly changing AI marketplace, difficulty validating vendors’ performance claims, and capacity constraints in testing and governing genAI use in policy settings. Difficulties with effectively managing and leveraging data (also called data readiness), fear of malicious genAI use, and challenges to creating effective guardrails and risk assessments are other obstacles local governments may face in adopting higher-tier genAI tools.
What do local governments need to adopt genAI more broadly?
We’ve compiled a repository of the available templates and resources that can help local governments use genAI to improve both their productivity and residents’ lives. Still, unmet needs remain and require investment and partnership to fill the gaps.
Local governments can engage with network organizations that support AI literacy and peer learning to build a broad foundation for genAI adoption. Targeted investments from technology companies and philanthropies can provide specialized capacity and testing resources to help local governments effectively and responsibly adopt higher-tier AI.
Let’s build a future where everyone, everywhere has the opportunity and power to thrive
Urban is more determined than ever to partner with changemakers to unlock opportunities that give people across the country a fair shot at reaching their fullest potential. Invest in Urban to power this type of work.